
An International Prime Meridian Conference was held in Washington, DC, in 1884 to standardize time around the world and select the Prime Meridian, or the meridian that is designated 0º from which all other longitudes are measured (often referred to as Greenwich Mean Time or GMT, because the place they chose as the Prime Meridian was Greenwich, England). finally began using Sir Fleming's standard time zones on November 18, 1883. He came to this idea because Earth completes a rotation every 24 hours and there are 360º of longitude, so each hour Earth rotates 1/24th of a circle or 15º.Īs with many new ideas, his solution was not immediately embraced. He proposed that the world be divided into 24 time zones, each spaced 15º (fifteen degrees) of longitude apart (like 24 sections of an orange). In 1878, Sir Sandford Fleming (1827–1915) developed the system of worldwide time zones that we still use today. This problem was particularly pronounced in the United States and Canada where transcontinental railroads moved people over thousands of miles relatively quickly.Ĭlearly, it is no surprise then that the person considered the father of standardized time was a Canadian railway engineer. In the early days of the railroads, train schedules were totally confusing because they were based on local solar time. Engineering TimeĪll that changed when railroads began to move people across great distances quickly. When they traveled to another town, they would simply change their watch when they arrived. Each town's citizens would set their clocks and pocket watches according to the official town clock or timekeeper. Noon was simply when the sun was directly overhead wherever you were, in what is called solar time.
Time Measurement, Time Zones, and the International Date Lineīefore the advent of railways in the 1800s, all time was local.
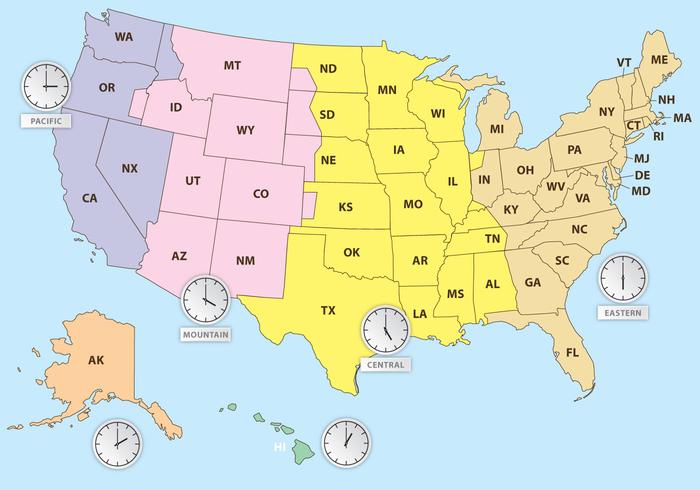
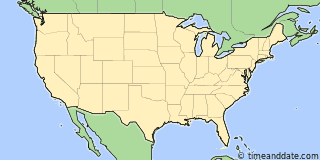
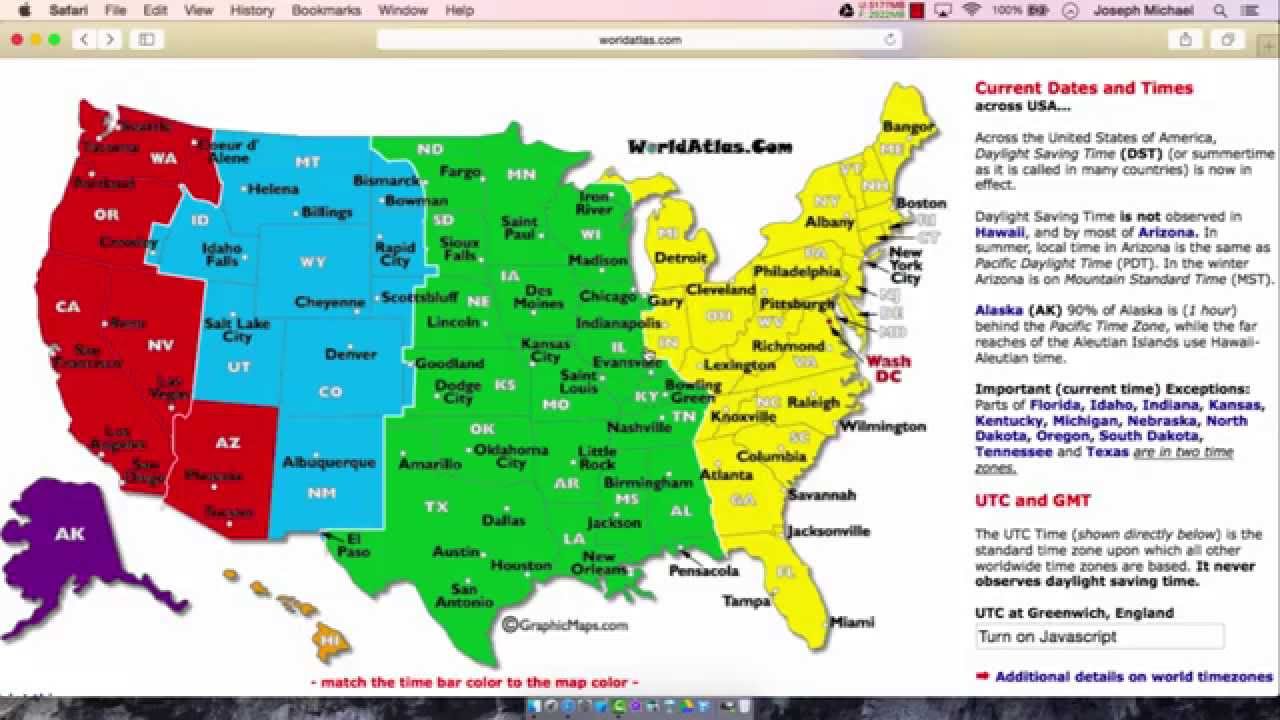
US TIME ZONE MAP CURRENT TIMES FULL SIZE
Map of world time zones – full size Related Links A transcontinental train schedule was the mother of invention


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
